Generalities
Realized by:
Dr HAMZA Lamia
Department of Mathematics and Computer Science
Educational Objectives

- Understand what an enterprise information system is;
a. Technical dimension
b. Organizational dimension
c. Managerial dimension
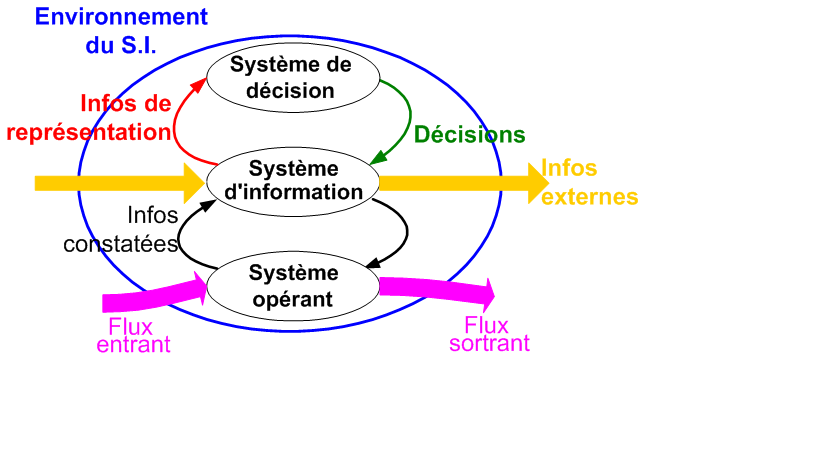
a. Steering system
b. Decision-making system
c. Operational system

Second-Year Bachelor's Students
Field: Computer Science
Prerequisites:

Basic Concepts of Algorithms
Course Presentation:
The information system (IS) can be defined as an organized set of resources (hardware, software, personnel, data, procedures, etc.) that allows for the acquisition, storage, processing, and communication of information in various forms within an organization.
First and foremost, there are individuals: these are all the people who use the system, whether they are regular employees or managers. There are also physical resources: these include all the physical devices used to receive, manipulate, and transmit information, as well as the media for that information, whether they are paper, magnetic, optical, or electronic.
Next, there are software and procedures: software refers to all the programs necessary for the operation of the information system (when it is computerized, of course). Finally, there are the data, which serve as the raw material for processing. Data can either be entered, in which case they correspond to new events for the information system, or calculated, serving as processing results.
Course Outline:
Chapter 1: Characteristics of a Business (different definitions, main functions, and various forms of business structure).
Chapter 2: Systems Approach to the Business (fundamental concepts of the systems approach, notion of a system, the different subsystems of the business, introduction to information systems (role, place, functional and structural aspects)).
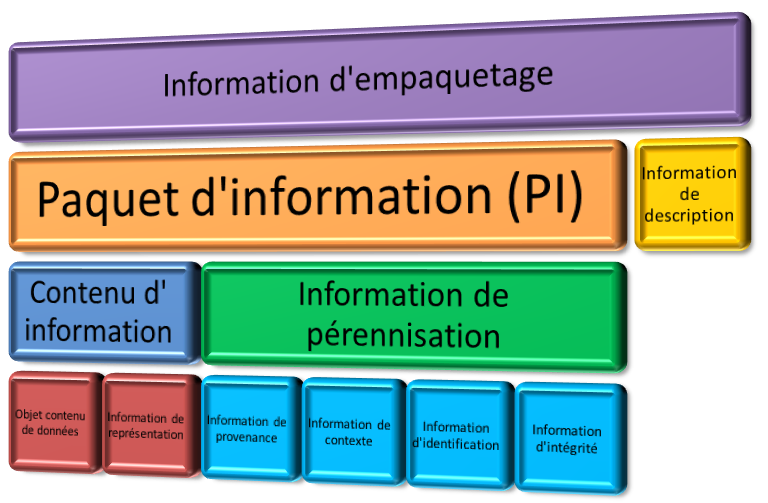
Chapter 3: Different Information Techniques (notion of information, representation of information, coding, control).
Chapter 4: Development of an Information System (process, life cycle, and development activities of an IS, classification of analysis and design methods for an IS, MERISE methodology).
Evaluation Method:
- TD Assessment: 25%
- TP Assessment: 25%
- Exam: 50%